
- PINEAPPLE CALORIES SKIN
- PINEAPPLE CALORIES FULL
Relish a cup of juicy pineapple slices as a snack along with other healthy approaches to lose weight.
PINEAPPLE CALORIES SKIN
There is no scientific evidence that pineapple skin helps in weight loss. So, eating pineapple does not make you fat.ĭoes boiled pineapple skin aid weight loss? February 27, 2009.Pineapple is a low-calorie and high-water content fruit. Why Can’t You Put Pineapple Pieces Into Jello? UCSB Science Line.American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. InformAll: Communicating About Food Allergies. Allergy Information for Pineapple ( Ananas comosus).University of Nebraska-Lincoln Food Allergy Research and Resource Program. Allergenic Foods and Their Allergens, With Links to InformAll: Fruits.National Center for Home Food Preservation.
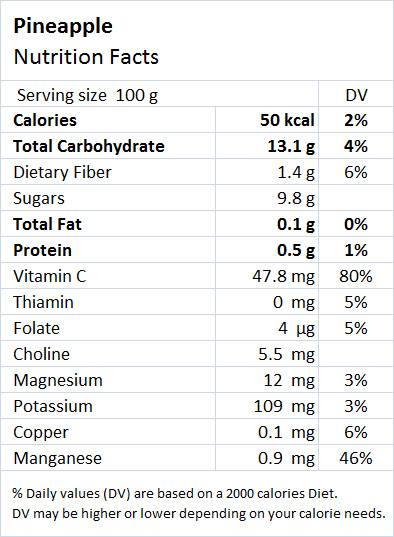 General Freezing Information: Thawing and Preparing Foods for Serving. National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Acute Protease Supplementation Effects on Muscle Damage and Recovery Across Consecutive Days of Cycle Racing. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine. Preventing c2c12 Muscular Cells Damage Combining Magnesium and Potassium With Vitamin D3 and Curcumin. Physiological and Molecular Study on the Anti-Obesity Effects of Pineapple (Ananas comosus) Juice in Male Wistar Rat. El-Shazly SA, Ahmed MM, Al-Harbi MS, et al. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology. Anti-inflammatory Properties of a Proprietary Bromelain Extract (Bromeyal) After In Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Bottega R, Persico I, De Seta F, et al. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease Across the Life Span. Pineapple (Ananas comosus): A Comprehensive Review of Nutritional Values, Volatile Compounds, Health Benefits, and Potential Food Products. Tropical Fruits and Their Co-Products as Bioactive Compounds and Their Health Effects: A Review. Sayago-Ayerdi S, Garcia-Martinez DL, Ramirez-Castillo AC, et al. But remember that pineapple is best consumed as part of an overall healthy, balanced diet, and eating too much of a single fruit doesn’t provide all of the nutrients you need for better health. Overall, there are promising health benefits associated with including pineapple in your diet. However, more human studies are needed with pineapple consumption - and not just bromelain extracts - to confirm such findings. An in vitro study suggested that bromelain extracts reduced inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, possibly leading to better outcomes in inflammatory bowel diseases and related cancers.
General Freezing Information: Thawing and Preparing Foods for Serving. National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Acute Protease Supplementation Effects on Muscle Damage and Recovery Across Consecutive Days of Cycle Racing. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine. Preventing c2c12 Muscular Cells Damage Combining Magnesium and Potassium With Vitamin D3 and Curcumin. Physiological and Molecular Study on the Anti-Obesity Effects of Pineapple (Ananas comosus) Juice in Male Wistar Rat. El-Shazly SA, Ahmed MM, Al-Harbi MS, et al. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology. Anti-inflammatory Properties of a Proprietary Bromelain Extract (Bromeyal) After In Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Bottega R, Persico I, De Seta F, et al. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease Across the Life Span. Pineapple (Ananas comosus): A Comprehensive Review of Nutritional Values, Volatile Compounds, Health Benefits, and Potential Food Products. Tropical Fruits and Their Co-Products as Bioactive Compounds and Their Health Effects: A Review. Sayago-Ayerdi S, Garcia-Martinez DL, Ramirez-Castillo AC, et al. But remember that pineapple is best consumed as part of an overall healthy, balanced diet, and eating too much of a single fruit doesn’t provide all of the nutrients you need for better health. Overall, there are promising health benefits associated with including pineapple in your diet. However, more human studies are needed with pineapple consumption - and not just bromelain extracts - to confirm such findings. An in vitro study suggested that bromelain extracts reduced inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, possibly leading to better outcomes in inflammatory bowel diseases and related cancers. 
This may be attributed to a naturally occurring enzyme in pineapple called bromelain. Better Gastrointestinal Health Research suggests people who regularly include pineapple in their diet also have fewer bowel problems and overall better gastrointestinal function.
PINEAPPLE CALORIES FULL
While no single food can ward off inflammation, eating a diet full of antioxidant-rich foods like pineapple may reduce your lifetime risk of inflammatory diseases, such as autoimmune disorders, cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and liver and kidney diseases. Decreased Inflammation Like other types of fruit, pineapple is high in antioxidants, a feature that may reduce inflammation in the body.Human studies are needed to determine if these potential effects are similar in people.

The authors also noted better cardiovascular health and lower inflammation as a result.
May Reduce Blood Cholesterol A preliminary review of several tropical fruits describes lower serum lipid profiles, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in rats who were given pineapple extract every day for 30 days. Aside from the healthy nutritional profile of pineapple, here’s what the current research says about the potential health benefits of this fruit:







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
